BrainDX
"사람들이 올바른 정보를 얻을 때 올바른 결정을 내릴 것입니다" - Thomas Jefferson
BrainDx, L.L.C.
BrainDX Normative Database
브레인디엑스 표준 데이터베이스
기능적 뇌 분석 보고서 생성 시스템
BrainDx는 QEEG 분야의 초기 연구자 중 일부의 연구를 포함합니다. BrainDx는 사고와 행동의 문제와 관련이있을 수 있으므로 뇌 기능 장애의 존재를 정의하는 데 도움을줍니다. 이 시스템은 모든 문화에 공통적 인 많은 신경 및 행동 조건의 치료를 최적화하기 위해 전 세계적으로, 저렴한 비용으로 그러한 정보를 이용할 수 있도록 설계되었습니다.
BrainDx는 정량적 전기 생리학 분야의 진화에서 파생 된 지식을 연구실에서 임상 실습으로 쉽게 번역 할 수 있도록하기 위해 국제적으로 인정 된 신경 생리학 연구자 및 임상의에 의해 형성되었습니다. 이러한 노력의 핵심은 연구 및 개발 뉴욕 대학교 의과 대학 Brain Research Laboratories에서 이 연구 결과는 국제적으로 수없이 많은 전문 사회 회의에서 발표 되었으며 학문 분야, 학술지, 교과서 전반에 광범위하게 광범위하게 발표되었으며 의료, 계측, 교육 및 법의학의 여러 분야에 적용되었습니다.
BrainDx는 고객이 정신 장애 및 신경 학적 조건과 관련하여 개인을 분류하는 데 도움이되는 여러 수준의 분석에서 뇌 기능을 평가할 수있는 모듈 시스템을 개발했습니다. 3 차원 근원 현지화 방법을 사용하여 수학적으로 가장 두드러진 기초 자료 인 두피 기록 데이터를 식별하여 장애의 병태 생리학을 더 잘 이해하고 의약품을 포함한 치료 기술의 최적화 및 평가를 돕습니다. BrainDx 기술은 임상의가 개인의 행동 및 수행 능력과 관련된 신경 기능 상태를 문서화하는 데 사용할 수있는 해석 보고서를 작성합니다.
보고서 생성 과정의 일부에는 환자의 뇌 기능 프로필 결과를 나이가 맞는 정상인 데이터베이스와 비교하는 과정이 포함됩니다. 그런 다음 환자의 병력 정보를 통합하여 개별 환자의 QEEG 프로파일을 알려진 장애가있는 환자와 비교하는 통계적 비교를 실시하고 환자가 통계적으로 그러한 환자와 유사 할 확률을 평가하여 진단 프로세스를 지원합니다. 또한, 최종 사용자가 치료 옵션의 우선 순위를 정하는 작업을 돕기 위해 이러한 프로파일을 기반으로 치료 적 개입에 대한 임상 지침을 제공 할 수 있습니다.
예를 들어, 환자가 기억 상실에 대한 일반적인 불만을 나타내거나 자신의 연구가 잘 진행되지 않는다고 말하면, BrainDx 시스템은 연령이 예상되는 정상 수치와 비교하여 객관적으로 뇌 기능을 평가할 수 있으며, 이 환자는 임상 우울증이있는 환자가 아닌 치매 환자의 환자와 일치합니다. 비 침습적 인 20-30 분 QEEG 뇌 평가는 특정 증상을 가진 환자가 비슷한 증상과 객관적인 진단을 가지고 데이터베이스에서 다른 환자와 일치 할 확률을 통계적 정확성과 함께 생성 할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 소아과 문제의 경우 학습 장애 (LD)를 자폐증 스펙트럼 장애 (ASD)에서 정상 또는 주의력 결핍 / 과잉 장애 (ADHD)와 구분하십시오. ,기타. 또한 BrainDx는 환자가 두 가지 상태에있을 때 뇌 기능을 평가할 수있는 능력을 제공합니다. 두 가지 상태 사이의 뇌 기능의 변화를 정량적으로 평가합니다 (예 : 약물 투여 및 중단).
이 소프트웨어 도구는 다양한 플랫폼에서 작동하도록 제공되며 전 세계의 연구 프로그램을위한 도구뿐만 아니라 다양한 임상 목적을 위해 합리적인 가격으로 제공됩니다. 몇 초 만에 EEG 데이터에서 찾고있는 답변을 얻고 뇌 - 행동 관계에 관한 다양한 질문을 탐색하십시오.
회사
BrainDx의 Mission은 포괄적이고 시의 적절하며 효율적이며 비용 효율적인 방식으로 전 세계 의료 전문가에게 자동화 된 QEEG 보고서를 제공하는 것입니다. BrainDx, L.L.C.의 파트너들의 믿음입니다. 는 환자의 검사로 수집 된 뇌파 데이터로부터 의미있는 해석 보고서 제공에 혁명을 일으킬 수있는 방식으로이 서비스를 제공 할 수있는 고유 한 위치에 있습니다.
BrainD L.L.C. 번역 연구를위한 모델입니다. 이 프레임 워크에서 실무자는 번역 시스템이 응용 연구보다 우수한 결과를 낼 수 있도록 어려운 문제에 대한 실제 관련 기준을 제공함으로써 연구 의제를 구체화 할 수 있습니다. 번영을 위해 번역 연구에는 지식 기반의 생태계가 필요합니다. 지식 생태계는 구성 요소가 조경의 모든 부분에서 사용할 수있는 데이터를 생성, 제공, 관리 및 분석합니다. 목표는 유용한 지식으로 데이터의 변환을 가속화하기위한 지속적인 피드백 루프입니다. 협업, 데이터 공유, 데이터 통합 ??및 표준은 매우 중요합니다.
번역 연구는 정보, 데이터가 병원, 진료소 및 연구 참가자로부터 체계적이고 체계적인 형식으로 저장소와 실험실로 흐를 것을 요구합니다. 이 데이터를 지속적으로 구조화하고 통합함으로써 NYU의 Brain Research Laboratory (BRL)는 뇌 관련 장애의 복잡하고 근본적인 원인을 탐구합니다. BrainDx는 효과적인 예방, 조기 발견 및 맞춤 치료를 위해 과학의 최첨단에서 지식의 생산적 사용을 촉진하는 BRL과의 관계에 종사자를 데려옵니다.
-
분석 : 규범 접근법
어린이 및 성인 규범은 출판 된 기사에서 설명한 것과 동일한 절차를 따랐습니다. 초기 표준은 정부 자금 지원 (BEH, NSF, NIA)에 따라 수행되었으며 포함 / 제외 기준 및 데이터 수집에 대한 엄격한 프로토콜을 따랐습니다 (자세한 내용은 간행물에 있음). 다음 사항을주의해야합니다.
규범은 회귀 방정식이 반쪽에 형성되고 다른 (독립적 인 복제)에서 테스트 된 회귀 방정식을 사용하여 구성되었습니다. 예상되는 "히트 수"(z 값 <0.05)보다 적은 값이 후반. 그 후 두 개의 반을 결합하고 최종 방정식을 구성했다. 대상을 더 추가 할 때까지 대상에 대상을 추가했다 (연령대를 넘어) 회귀 방정식을 변경하지 않았다. 따라서 규범화 될 필요가있는 인구의 크기는 통계적으로 결정되었다. 기대했던 것보다 더 많은 어린이들이 성인보다 더 빨리 (연령에 따라 급격한 변화가 필요함) 요구되었습니다.
추가적인 평가는 높은 테스트 / 재시험의 안정성과 표준의 안정성을 입증하기 위해 사용되었습니다. 초기 표준화 이후 추가로 어린이 및 성인 인구에 증폭기 등의 발전을 나타내는 주제가 추가 된 지 몇 년이 지났습니다.
모든 새로운 피험자는 초기 프로젝트와 동일한 기준에 따라 모집되었습니다.
분석 : 로레타 규범
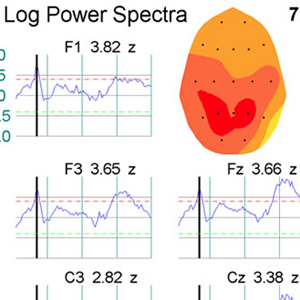
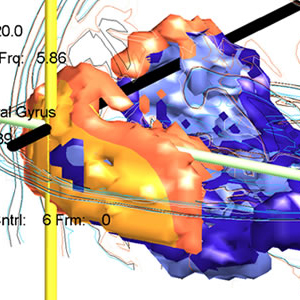
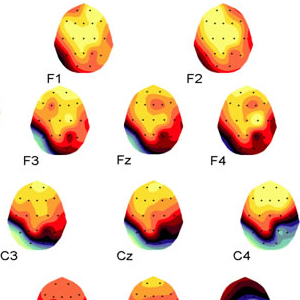
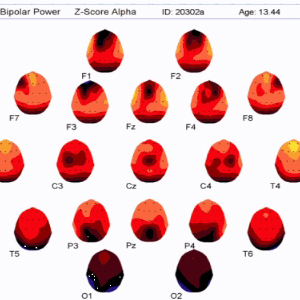
LORETA (저해상도 전자기 단층 촬영 분석)는 두피에서 기록 된 전압의 수학적으로 가장 가능성이 높은 소스를 현지화하기위한 소스 위치 파악 역 문제 방법입니다. BRL에서 Roberto Pascual-Marqui와 함께 작업하면서 복셀 표준은 동일한 BRL / NYU 표준 데이터베이스를 사용하여 계산되었습니다 Neurometrics에 설명 된 방법론은 sLORETA 표준에 적용되어 모델에서 각 복셀의 z- 변형을 허용하여 수학적으로 가장 가능성있는 뇌 보호기의 기본 소스의 통계적 색상 코딩 이미지로 표시 할 수 있습니다. 각 복셀에 대해 개인의 값은 연령에 대한 예상 표준과 통계적으로 비교됩니다. 각 보셀에 대한 통계적 유의성은 확률 론적 MRI Atlas의 조각에 겹쳐진 색상으로 인코딩됩니다. 기존의 신경 영상 및 EEG 소스 위치 파악과 유사한 결과를 보여주는 광범위한 문헌이 존재합니다. 개발 된 연령 회귀 방정식은 양적 뇌파 측정을 표준화하여 피험자 연령과 무관하게 해석 될 수 있도록 도와줍니다. 아래의 sLORETA 이미지는 16 ~ 80 세 (N = 154)의 나이와 함께 대상과 관련된 상대 습득 회색 물질 복셀의 상관 관계를 나타내는 그림입니다. 회귀는 나이의 대수와 선형 (직선 적합)입니다. 각각의 양은 회백질 양의 20 %를 차지한다. 적색 볼륨의 모든 복셀은 주파수 17.2Hz에서 .48보다 큰 나이와 양의 상관 관계가 있습니다. .58의 최대 값은 왼쪽 Insula에 있습니다. 청색 부피의 모든 복셀은 10.2 Hz의 주파수에서 -44 미만의 상관 관계를가집니다. 일반적으로 이것은 측두엽의 베타가 증가하고 나이가 증가함에 따라 알파가 감소 함을 보여줍니다. 각 복셀의 현재 밀도 추정치는 뇌파의 총 에너지로 나눠지고 (따라서 주관적 상대 강도), 따라서이 측정에서 뇌파의 전체 크기의 영향을 제거합니다.
기능 계산
기능 계산 : 전력 스펙트럼 및 다음을 포함한 관련 기능 :
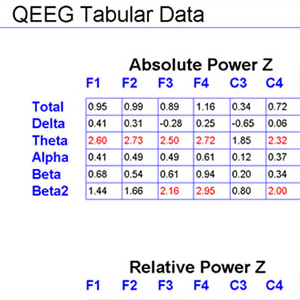
• 절대 파워 Absolute power
• 상대 파워 Relative power
• 평균 빈도 Mean frequency
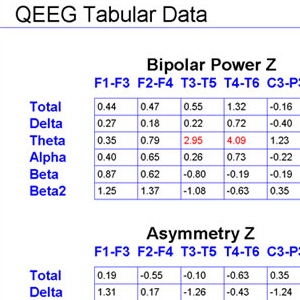
• 반 구간 대칭 Intra- and Inter-hemispheric symmetry
• 반 구간 일관성 Intra- and Inter-hemispheric coherence
소스 영역화
• LORETA 관심 지역 (ROI)에서 측정.
• 좁은 주파수 대역의 경우,
• precisley 시간 코딩 이벤트.
* 추가 비선형 기능에는 복잡성 및 연결성 측정이 포함됩니다.
각 대역 통과에 대해 계산 됨
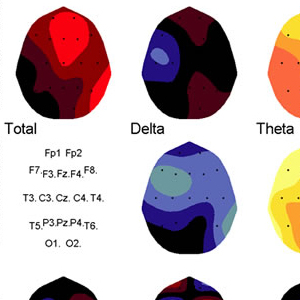
• 델타 (1.5-3.5Hz)
• 세타 (3.5-7.5Hz)
• 알파 (7.5-12.5Hz)
• 베타 (12.5-25Hz) 및 베타 2 (25-35Hz)
* 추가 비선형 기능에는 복잡성 및 연결성 측정이 포함됩니다.
Neurometrics에서 사용되는 방법 :
• 국제 10/20 배치 시스템의 19 개 지역에서 수집 된 디지털 EEG • 5000Ω 미만의 임피던스
• 링크드이어로 참조 됨
• 밴드 패스 = 0.5 ~ 50Hz, 샘플 속도> = 100Hz
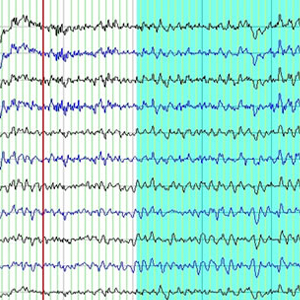
• 20-30 분. EEG 기록
• 상태 = 눈감고 • 아티팩트가 없는 1-2분의 데이터 선택
BrainDX 연구
- 제품
BrainDx는 Neurometric Analysis를 기반으로 해석 보고서를 작성하는 소프트웨어를 개발했습니다. 양적 뇌파 검사 (QEEG)를위한이 도구는 소프트웨어 기반의 의료 기술로 여러 정신병, 발달 및 신경계 뇌 질환의 진단 및 치료 모니터링을 용이하게합니다.
- 과학 기술
유익없는 디지털 뇌파 계측 (EEG) 입력의 2 ~ 3 분은 DSM / ICD로 진단 된 뇌 기능 장애를 가진 10,000 명 이상의 환자를 대상으로 한 계속해서 세련되고 확장 된 표준 데이터베이스 및 임상 데이터베이스와 비교됩니다. 개별 환자 기록에서 얻은 다른 데이터 외에도 소프트웨어는 대화 형으로 모든 컴퓨터에서 임상 보고서를 생성합니다.
- 용도
데이터는 대부분의 상업용 뇌파 장비에서 생성 된 파일에서 가져옵니다 (번역 된). 모든 변환기는 전달 함수 (주파수 응답)의 중요한 차이를 보완하도록 조정되었습니다. 결과는 주석이 달린 그림, 문서 및 임상 관찰을 삽입 할 수있는 기회가있는 구조화되고 조정 가능한 형식으로 제공됩니다.
- 판별 함수
판별 함수 (Discriminant functions)는 다양한 장애가있는 환자 그룹에 대한 광범위한 연구에서 발견되는 환자의 프로파일과 특징 패턴 간의 유사성을 정량적으로 추정합니다. 이 알고리즘에 의한 분류는 환자 병력에 표시된 진단이나 증상과 관련된 장애로 제한됩니다
- 정량화 뇌파 평가 :
정량화 뇌파 평 결과는 이 연령대의 예상 수치로부터 두뇌 활동의 전기 생리 학적 측정치의 통계적 편차를 나타냅니다. 표시된대로 뇌 영역의 기능 장애는 일반적으로 기능적 또는 행동 적 문제에 해당합니다. 가능한 경우에는 기능적 또는 행동 장애를 묘사하고 후속 치료로부터 치료 효능을 확립하기 위해 사용될 수있는 전처리 수행 수준을 확립하기 위해 신경 심리 검사가 고려되어야한다. 이 보고서는 임상 적 사용을위한 지침을 제공하기위한 것이므로 임상 진단이나 치료 선택을위한 유일한 정보 출처로 사용되어서는 안됩니다. BrainDx는 서비스 제공자에 대한 본 보고서의 진술에 기인 한 임상 진단상의 오류나 치료 실패에 대해 책임을지지 않습니다. 임상가가 간질의 존재에 대해 염려해야한다면, 신경 학적 이상이나 아래에 기술 된 결과가 통상적 인 뇌파 의뢰가 보장 될 수 있습니다.
BrainDX 평가의 기초
BrainDx는 시스템 이론의 역사적인 응용 프로그램과 이미징 및 통계 예측의 최첨단 발전을 결합합니다.
유효성 (Validity) - 의미 있고 관련성이 있는 측정이 얼굴과 구조 모두에서 수렴 될 수 있는 정확성.
신뢰성 - 테스트 테스트 및 교차 검증을 통합하는 측정 방법을 사용하여 조건 또는 결과의 재현성.
모든 새로운 피험자는 초기 프로젝트와 동일한 기준에 따라 모집되었습니다.
다 변수 측정 : Z- 점수를 사용하면 다 변수 "시스템"기능을 계산할 수있는 공통 메트릭을 사용할 수 있습니다. 이러한 다 변수 계산은 비정상적인 정도와 같은 개념을 요약 할 때 종종 중요한 기능의 수퍼 세트를 형성하며 아래에 설명 된 판별 함수에 중요한 기여를 합니다.
BrainDX DataBase Price & Order
브레인디엑스 표준 뇌파 데이터베이스 구입시 문의 후 주문바랍니다.
참고문헌 (Bibliography)
신경 계측학( Neurometrics) 및 규범의 배경 및 역사
John ER, Karmel BZ, Corning WC, Easton P, Brown D, Ahn H, John M, Harmony T, Prichep LS, Toro A, Gerson I, Thatcher RW, Valdes P, Kaye H, Valdes P, Schwartz E. Neurometrics: Numerical taxonomy identifies different profiles of brain functions within groups of behaviorally similar people. Science 1977; 196: 1383-410.
John ER, Karmel BZ, Prichep LS, Ahn H, John M. Neurometrics applied to the quantitative electrophysiological measurement of organic brain dysfunction in children. In: Shagass C, ed. Psychopathology and Brain Dysfunction. Raven Press; 1977
John ER, Prichep LS, Ahn H, Easton P, Karmel BZ, Thatcher R, Toro A. Neurometrics: Quantitative electrophysiological measurement of organic brain dysfunction in children. In: Shagass C, ed. Psychopathology and Brain Dysfunction. Raven Press; 1977.
John ER, Karmel BZ, Corning, Easton P, Brown D, Ahn H, John M, Harmony T, Prichep LS, Toro A, Gerson I, Bartlett F, Thatcher R, Kaye H, Valdes-Sosa P, Schwartz E. Neurometrics: Computerized diagnosis and remediation of brain dysfunctions. In: Chacko GK, ed. Health Handbook. Amsterdam: N. Holland Publishing; 1979: 330-481.
Ahn H, Prichep LS, John ER, Baird H, Trepetin M, Kaye H. Developmental equations reflect brain dysfunction. Science 1980; 210: 1259-62.
John ER, Ahn H, Prichep LS, Trepetin M, Brown D, Kaye H.Developmental equations for the electroencephalogram.Science 1980; 210: 1255-8.
Ahn H, Prichep L, John ER. Electroencephalogram tests for brain dysfunction: A question of validity. Science 1982; 217: 82.
John ER, Prichep LS, Ahn H, Easton P, Fridman J, Kaye H. Neurometric evaluation of cognitive dysfunctions and neurological disorders in children. Progress in Neurobiology 1983; 21: 239-90.
Prichep LS, John ER.Neurometrics: Clinical Applications. In: Lopes Da Silva F, van Leeuwen WS, Remond A, eds. Handbook of Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, Vol. 2. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1986: 153-70.
John ER, Prichep LS, Easton P. Normative data banks and Neurometrics: Basic concepts, methods and results of norm construction. In: Gevins AS, Remond A, eds. Handbook of Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, Vol. I. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1987: 449-95.
Volkow ND, Gomez-Mont F, Inamdar M, Lamella M, Prichep L, John ER. Multivariate Analysis of the EEG in normal adolescents.Biol Psychiatry 1987; 22: 199-204.
John ER, Prichep LS. Principles of neurometrics and neurometric analysis of EEG and evoked potentials. In: Niedermeyer E, Lopes Da Silva F, eds. EEG: Basic Principles, Clinical Applications and Related Fields. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins; 1993: 989-1003.
John ER, Zhang Z, Brodie JD, Prichep LS. Statistical probability mapping of brain function and structure. In: Thatcher RW, Hallett M, Zeffiro T, John ER, Huerta M, eds. Functional Neuroimaging: Technical Foundations. Academic Press; 1994: 137-43.
Hughes, J. R. & John, E. R. (1999). Conventional and quantitative electroencephalography in psychiatry. J Neuropsychiatry ClinNeurosci, 11, 190-208.
Koenig T, Prichep LS, Lehmann D, Valdes-Sosa P, Braeker E, Kleinlogel H, Isenhart R, John ER. Millisecond by Millisecond, Year by Year: Normative EEG Microstates and Developmental Stages.Neuroimage 2002; 16: 41-8.
John ER, Prichep LS, Friedman J, Easton P. Neurometrics: Computer-assisted differential diagnosis of brain dysfunctions. Science 1988; 293: 162-9.
Prichep LS. Use of normative databases and statistical methods in demonstrating clinical utility of QEEG: Importance and cautions. Clinical EEG 2005; 36: 82-7.
Alper KA, John ER, Brodie J, Gunther W, Daruwala R, Prichep LS.Correlation of PET and QEEG in normal Subjects. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging 2006; 146: 271-82.
John ER, Prichep LS. The Relevance of QEEG to the Evaluation of Behavioral Disorders and Pharmacological Interventions.Clinical EEG and Neuroscience 2006; 37: 135-43.
John ER, Prichep LS. Principles and applications of quantitative electroencephalogram in psychiatry. In: Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, Ruiz P, eds. Kaplan and Sadock’s Comprehensive Textbook of Psychiatry. 9th edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2009: 1013-32.
Congedo M, John ER, De Ridder D, Prichep LS, Isenhart R. Group independent component analysis of resting-state EEG in large normative samples. International Journal of Psychophysiology 2010; 78(2): 88-99.
Congedo M, John ER, De Ridder D, Prichep LS, Isenhart R. On the “Dependence” of “Independent” Group EEG Sources; an EEG Study on Two Large Databases. Brain Topography 2010; 23(2):134-138.
- Source Localization
Prichep LS, John ER, Tom M. Localization of deep white matter lymphoma using VARETA ? A case study. Clinical EEG 2001; 32: 62-6.
Bosch-Bayard, J., Valdes-Sosa, P., Virues-Alba, E., Aubert-Vazquez, E., John, E. R., Harmony, T., Riera-Diaz, J., & Trujillo-Barreto, N. (2001). 3D Statistical Parametric Mapping of EEG Source Spectra by means of Variable Resolution Electromagnetic Tomography (VARETA).Clin EEG, 32, 47-61.
Alper K, Raghavan M, Isenhart R, Howard B, Doyle W, John ER, Prichep LS. Localizing epileptogenic regions in partial epilepsy using three-dimensional statistical parametric maps of background EEG source spectra.Neuroimage 2008; 39: 1257-65.
Pascual-Marqui RD, Lehmann D, Koukkou M, Kochi K, Anderer P, Saletu B, Tanaka H, Hirata K, John ER, Prichep LS, Biscay-Lirio R, Kinoshita T. Assessing interactions in the brain with exact low-resolution electromagnetic tomography. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 2011; 369: 3768-3784.
- Chemical Dependency
Alper KR, Prichep LS, Kowalik SC, Rosenthal MS. Persistent QEEG abnormality in crack cocaine users at 6 months of drug abstinence. Neuropsychopharm. 1998; 19: 1-9.
Prichep LS, Alper KR, Kowalik SC, Vaysblat L, Merkin HA, Tom M, John ER, Rosenthal MS. Prediction of treatment outcome in cocaine dependent males using quantitative EEG. Drug Alc.Depend. 1999; 54: 35-43.
Prichep LS, Alper KR, Sverdlov L, Kowalik SC, John ER, Merkin HTM, Howard B, Rosenthal MS. Outcome related electrophysiological subtypes of cocaine dependence. Clinical EEG 2002; 33: 8-20.
Reid MS, Prichep LS, Ciplet D, O’Leary SO, Tom M, Howard B, Rotrosen J, John ER. Quantitative electroencephalographic studies of cue-induced cocaine craving. Clinical EEG 2003; 34: 1-14.
Reid MS, Flammino F, Howard B, Nilsen D, Prichep LS. Topographic imaging of Quantitative EEG in response to smoked cocaine self-administration in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006; 31: 872-4.
Reid MS, Flammino F, Howard B, Nilsen D, Prichep LS. Cocaine cue versus cocaine dosing in humans: Evidence for distinct neurophysiological response profiles. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 2008; 91: 155-64.
Alper K, Shah J, Howard B, John ER, Prichep LS. Childhood abuse and EEG source localization in crack cocaine dependence. Psychiatry Research:Neuroimaging. 2013;213:63-70
- Cerebral Ischemia
Jonkman, E. J., Poortvliet, D. C. J., Veering, M. M., DeWeerd, A. W., & John, E. R. (1985). The use of neurometrics in the study of patients with cerebral ischemia. ElectroencephalogrClinNeurophysiol, 61, 333-341.
Veering, N. M., Jonkman, E. J., Poortvliet, D. C., de Weerd, A. W. , Tans, J. T., & John, E. R. (1986). The effect of reconstructive vascular surgery on clinical status, quantitative EEG and cerebral blood flow in patients with cerebral ischaemia. A three month follow-up study in operated and unoperated stroke patients. EEG ClinNeurophysiol, 64, 383-393.
John ER, Prichep LS, Chabot RJ, Isom WO. Monitoring brain function during cardiovascular surgery: Hypoperfusion vs. microembolism as the major cause of neurological damage during cardiopulmonary bypass. Heart and Brain, Brain and Heart. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 1989.
- Learning Disabilities/ADHD/Child-Adolescent Psychiatry
Baird, H. W., John, E. R., Ahn, H., & and Maisel, E. (1980). Neurometric evaluation of epileptic children who do well and poorly in school. EEG ClinNeurophysiol, 48, 683-693.
Kaye H, John ER, Ahn H, Prichep LS.Neurometric evaluation of learning disabillities.Intl.J.Neurosci. 1981; 13: 15-25.
John ER, Prichep LS, Fridman J, Ahn H, Kaye H, Baird H. Neurometric evaluation of brain electrical activity in children with learning disabilities. In: Duffy F, Geschwind N, eds. Dyslexia: A Neuroscientific Approach to Clinical Evaluation. Boston: Little, Brown & Co.; 1985: 157-85.
Lewis AL, Pincus JH, Bard B, Richardson E, Prichep LS, Feldman M, Yeager C. Neuropsychiatric, psychoeducational and family characteristics of 14 juveniles condemned to death in the U.S. Am J Psychiatry 1988; 145: 584-9.
John ER, Prichep LS, Ahn H, Kaye H, Brown D, Easton P, Karmel Z, Toro A, Thatcher R. Neurometric Evaluation of Brain Function in Normal and Learning Disabled Children. Ann Arbor, Univ. of Michigan Press; 1989.
Chabot RJ, Prichep LS, John ER.The clinical role of neurophysiology in child and adolescent psychiatry. In: Noshpitz JD, ed. Handbook of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 1996.
Chabot RJ, diMichele F, Prichep LS, John ER. The clinical role of computerized EEG in the evaluation and treatment of learning and attention disorders in children and adolescents. J Neuropsychiatry Clinical Neuroscience 2001; 13: 171-86.
di Michele F, Prichep LS, John ER, Chabot RJ. The neurophysiology of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. International Journal of Psychophysiology 2005; 58: 81-93.
Chabot RJ, di Michele F, Prichep LS. The role of quantitative electroencephalography in child and adolescent psychiatric disorders.Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America 2005;14:21-53.
Chabot RJ, Orgill AA, Crawford G, Harris MJ, Serfontein G. Behavioral and Electrophysiological predictors of treatment response stimulants in children with attention disorders. J Child Neurology 1999;14:343-351.
Chabot RJ, Merkin H, Wood LM, Davenport TL, Serfontein G. Sensitivity and Specificity of QEEG in Children with Attention Deficit or Specific Developmental Learning Disorders.Clin EEG 1996;27:26-34.
Chabot RJ, Serfontein G. Quantitative EEG profiles of children with Attention Deficit Disorder. BiolPsychiat 1996;40:951-963.
Chabot RJ, Sigal LH. QEEG and evoked potentials in central nervous systemlyme disease. Clin EEG 1995;26:137-145.
Coben R, Chabot RJ, Hirshberg L. EEG Analyses in the Assessment of Autistic Disorders. In: Casanova MF, El-Baz AS, Suri JS, eds. Imaging the Brain in Autism. Springer New York; 2013;349-370.
Chabot RJ, Coben R, Hirshberg L, Cantor D.S. QEEG and VARETA based Neurophysiological Indices of Brain Dysfunction in Attention Deficit and Autustic Spectrum Disorder. Austin J Autism & Relat Disabil 2015; Volume 1 Issue 2.
- Consciousness and Mental Activity
John ER, Prichep LS, Katz J, Easton P, Chabot R. Topographic maps of EEGs coherence and EP factor structure at rest and during mental tasks. In: Takahashi R, Flor-Henry
J, Gruzelier J, Niwa S, eds. Cerebral Dynamics, Laterality and Psychopathology. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1987.
John ER, Prichep LS, Chabot RJ. Quantitative Electrophysiological Maps of Mental Activity.Brain Dynamics 2 edn. 1989: 316-30.
John ER, Prichep LS, Chabot RJ. Quantitative electrophysiological maps of mental activity. In: Basar E, Bullock TH, eds. Dynamics of Sensory and Cognitive Processing by the Brain. Springer-Verlag; 1989.
Prichep LS, John ER, Easton P, Chabot R. Cross-spectral coherence at rest and during mental activity. In: John ER, ed. Machinery of the Mind. Boston: Birkhauser; 1990: 471-8.
John ER, Halper JP, Lowe RS3, Merkin H, DeFina P, Prichep LS. Source Imaging of QEEG as a bedside method to detect awareness in a patient in a vegetative state. Brain Injury 2011; 25[4], 426-432.
- Anesthesia ? Loss and Return of Consciousness
Prichep LS, John ER, Chabot RJ, Gugino LD, Kox W. PSI Prediction of “arousal” events during surgery under continuous intravenous, inhalation or nitrous/narcotic anesthesia. Memory and Awareness in Anesthesia. Harrow: 1998.
Prichep LS, John ER, Gugino LD, Kox W, Chabot R. Quantitative EEG assessment of changes in the level of the sedation/hypnosis during surgery under general anesthesia: I. The Patient State Index (PSI). In: Jordan C, Vaughan DJA, Newton DEF, eds. Memory and Awareness in Anesthesia. IV edn. London: Imperial College Press; 2000: 97-102.
John ER, Prichep LS, Gugino LD, Kox W, Chabot RJ. Quantitative electroencephalographic (QEEG) changes accompanying loss and return of consciousness during inhalation anesthesia: II. Variable resolution electromagnetic tomography (VARETA).Memory and Awareness in Anesthesia IV. Northwick Park, Harrow, London: Imperial College Press; 2000: 102-7.
Gugino LD, Chabot RJ, Prichep LS, John ER, Formanek V, Aglio LS. Quantitative EEG changes associated with loss and return of consciousness in healthy adult volunteers anesthetized with propofol or sevoflurane. British J.Anaesth.2001; 87: 421-8.
John ER, Prichep LS, Kox W, Valdes-Sosa P, Bosch-Bayard J, Aubert E, Tom M, di Michele F, Gugino LD. Invariant reversible QEEG effects of anesthetics. Consciousness and Cognition 2001; 10: 165-83.
Drover D, Lemmens HJ, Pierce ET, Loyd G, Ornstein E, Prichep LS, Chabot RJ, Gugino L. Patient state index: titration of delivery and recovery from propofol, alfentanil, and nitrous oxide anesthesia. Anesthesiology 2002; 97: 82-9.
Prichep LS, Gugino LD, John ER, Chabot RJ, Howard B, Merkin HA, Tom M, Wolter S, Rausch L, Kox W. The Patient State Index (PSI) as an indicator of the level of hypnosis under general anesthesia. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2004; 92: 393-9.
Rundshagen I, Schroder T, Prichep LS, John ER, Kox WJ. Changes in cortical electrical activity during induction of anaesthesia with thiopental/fentanyl and tracheal intubation.A quantitative electroencephalographic analyses. British J.Anaesth.2004; 92: 33-8.
John ER, Prichep LS. The anesthetic cascade: how anesthesia suppresses awareness. Anesthesiology 2005; 102: 447-71.
Kox W, von Heymann C, Heinze J, Prichep LS, John ER, Rundshagen I. Electroencephalographic mapping during routine clinical practice: cortical arousal during tracheal intubation? Anesthesia and Analgesia 2006; 102: 825-31.
- Adult Psychiatric Disorders and Neurological Disorders
Prichep LS, Mas F, Hollander E, Liebowitz M, John ER, Almas M, DeCaria CM, Levine RH. Quantitative electroencephalographic subtyping of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Res. 1993; 50 : 25-32.
Prichep LS, John ER, Alper K, Gomez-Mont F, Essig-Peppard T, Flitter M. Quantitative EEG in depressive disorders. In: Shagass C, Josiassen RC, and Roemer RA, eds. Brain Electrical Potentials and Psychopathology. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1986: 223-44.
Prichep LS.Neurometric QEEG measures of depressive disorders. In: Takahashi P, Flor-Henry J, eds. Cerebral Dynamics, Laterality and Psychopathology. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1987: 55-69.
Prichep LS, Mas F, John ER, Levine R. Neurometric subtyping of obsessive compulsive disorders. In: Stefanis CN, Rabavilas AD, Soldatos CR, eds. Psychiatry: A World Perspective. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1990: 557-62.
Lieber AL, Prichep LS. Diagnosis and subtyping of depressive disorders by quantitative electroencephalography I: Discriminant analysis of selected variables in untreated depressives. The Hillside J of Clin.Psychiat.1988; 10: 71-83.
Prichep LS, John ER, Essig-Peppard T, Alper KR. Neurometric subtyping of depressive disorders. In: Cazzullo CL, Invernizzi G, Sacchetti E, Vita A, eds. Plasticity and Morphology of the CNS. London: M.T.P. Press; 1990.
Prichep LS, John ER, Mas F, Essig-Peppard T. Subtyping of Schizophrenia. In: John ER, ed. Machinery of the Mind. Birkhauser; 1990: 460-70.
Bolwig TG, Hansen ES, Hansen A, Merkin H, Prichep LS. Toward a better understanding of the pathophysiology of OCD SSRI responder: QEEG source localization. ActaPsychiatrScand 2007; 115: 237-42.
Prichep LS, John ER. QEEG profiles of psychiatric disorders. Brain Topography. 1992; 4: 249-257
Hansen ES, Prichep LS, Bolwig TG, John ER. Quantitative electroencephalography in OCD- patients treated with paroxetine. Clinical EEG 2003; 34: 70-4.
John ER, Prichep LS, Almas M. Subtyping of psychiatric patients by cluster analysis of QEEG.Brain Topogr. 1992; 4 : 321-326.
John ER, Prichep LS, Alper KR, Mas FG, Cancro R, Easton P, Sverdlov L. Quantitative electrophysiological characteristics and subtyping of schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry 1994; 36: 801-26.
John ER, Prichep LS, Valdes-Sosa P. Neurometric EEG classification and subtyping of psychiatric disorders. EEG Clin.Neurophysiol. 1997; 103: 36.
Mas F, Prichep LS, John ER, Levine R. Neurometric QEEG subtyping of obsessive compulsive disorder. In: Maurer K, ed. Imaging of the Brain in Psychiatry and Related Fields. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 1993: 277-80.
Alper K, Gunther W, Prichep LS, John ER, Brodie J. Correlation of QEEG with PET in Schizophrenia.Neuropsychobiology 1998; 38: 50-6.
Brasic JR, Zagzag D, Kowalik S, Prichep LS, John ER, Barmett JY, Bronson B, Nadrich RH, Cancro R, Buchsbaum M, Brathwaite C. Clinical Manifestations of Progressive Catatonia.German Journal of Psychiatry 2000; 3: 24.
John ER, Prichep LS, Winterer G, Hermann WM, diMichele F, Halper J, Bolwig T, Cancro R. Electrophysiological subtypes of psychotic states. ActaPsychiatrica Scandinavia 2007; 116: 17-35.
Prichep LS, John ER, Howard B, Merkin H, Hiesiger E. Assessment of pain using Quantitative EEG source imaging. Pain Medicine.2011; 12: 1241-48.
Prichep LS, John ER, Howard B, Merkin H, Hiesiger E. Evaluation of the pain matrix using EEG source localization: a feasibility study. Pain Medicine 2011;12:1241-1248.
Chabot RJ, Sigal LH. QEEG and evoked potentials in central nervous system lyme disease. Clin EEG 1995;26:137-145.
- Aging and Dementia
Prichep LS, Gomez-Mont F, John ER, Ferris SH. Neurometric Electroencephalographic characteristics of dementia. In: Reisberg B, ed. Alzheimer’s Disease: The Standard Reference. The Free Press (MacMillan); 1983: 252-7.
John ER, Prichep LS. Neurometric studies of aging and cognitive impairment. In: Uylings HBM, Van Eden CGV, De Bruin JPC, Corner MA, Feenstra MGP, eds. The Prefrontal Cortex. Progress in Brain Research. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1990: 545-55.
Prichep LS, John ER, Ferris SH, Reisberg B, Alper KR, Cancro R. Quantitative EEG correlates of cognitive deterioration in the elderly. Neurobiology Aging 1994; 15: 85-90.
Koenig T, Prichep LS, Dierks T, Hubl D, Wahlund LO, John ER, Jelic V. Decreased EEG synchronization in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiology of Aging 2005; 26: 165-71.
Prichep LS, John ER, Ferris SH, Rausch L, Fang Z, Rausch L, Cancro R, Torrossian C, Reisberg B. Prediction of longitudinal cognitive decline in normal elderly with subjective complaints using electrophysiological imaging. NeuroBiol Aging 2006; 27: 471-81.
Prichep LS.Quantitative EEG and Electromagnetic Brain Imaging in Aging and in the Evolution of Dementia.Ann.N.Y.Acad Sci. 2007; 40: 1-12.
Lehmann C, Koenig T, Jelic V, Prichep LS, John ER, Walhlund L, Dodge Y, Dierks T. Application and comparison of classification algorithms for recognition of Alzheimer’s disease in electrical brain activity (EEG). Journal of Neuroscience Methods 2007; 161: 342-50.
Reisberg B, Prichep LS, Mosconi L, John ER, Glodzik-Sobanska L, Boksay I, Monteiro I, Torossian C, Vedvyas A, Ashraf N, Jamil IA, de Leon MJ. The pre-mild cognitive impairment, subjective cognitive impairment stage of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s and Dementia 2008; 4: S98-S108.
- Treatment Applications
Cantor, D.S. An Overview of Quantitative EEG and Its Applications to Neurofeedback. In J. Evans (Ed.) Introduction to Neurofeedback.
New York: Academic Press, 1999.
Cantor, D.S. & Stevens, E. QEEG Correlates to Auditory-Visual Entrainment In Refractory Depression ? Journal of Neurotherapy, 13,100-108, 2009
Cantor,D. Applying advanced methods in clinical practice. In Budzynski, T, Budzynski, H., Evans, J. and Abarbanel, A. Introduction to Quantitative EEG and Neurofeedback: Advance Theory and Applications, 2nd Ed. Academic Press, 2009, 63-81.
Cantor, D. & Evans, J. (Eds.) Clinical Methods of Neurotherapy: Techniques and Treatment Applications. Elsevier Press, In press, 2013.